Functions¶
If a task has to be performed in a program many times, it is better to code that task as a function. Function is a piece of reusable code that can be invoked(called) from anywhere. They perform the intended task with supplied parameters and return the result if needed.
Python function has several advanatages over C functions and
Java methods: - Functions can take variable number of arguments.
This is supported natively - Functions can have named arguments (you had
seen it in print()) - Functions can return multiple values - If you
need a helper function for a function, you can define it inside the
function
Defining a function¶
The syntax for defining a function is as follows
def function_name(argument_list):
statement_1
statement_2
...
statement_n
return values
Let’s write a function for calculating 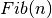 ,
, 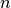 ‘th
Fibonacci Number, defined by
‘th
Fibonacci Number, defined by
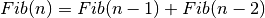 , where
, where 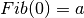 and
and
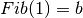
First implementation uses 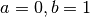 . Further implementations
include options for modifying
. Further implementations
include options for modifying  and
and 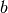
In [2]:
def fibonacci_first(n):
first,second = 0,1
while n != 0:
n, first, second = n - 1, second, first + second
return first
In [3]:
fibonacci_first(10) # Function call
Out[3]:
55
Let’s have an option to choose  and
and 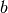
In [4]:
def fibonacci_second(n,a,b):
first,second = a,b
while n != 0:
n, first, second = n - 1, second, first + second
return first
In [5]:
fibonacci_second(9,1,1)
Out[5]:
55
Let  and
and 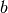 have the default values
have the default values 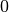 and
and
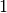 respectively
respectively
In [6]:
def fibonacci_third(n,a=0,b=1):
first,second = a,b
while n != 0:
n, first, second = n - 1, second, first + second
return first
In [7]:
fibonacci_third(10) # behaves like fibonacci_first()
Out[7]:
55
In [8]:
fibonacci_third(9,1) # behaves like fibonacci_second(9,1,1)
Out[8]:
55
In [9]:
fibonacci_third(9,1,2) # Run with fully different parameters
Out[9]:
89
You can also change one default value. You can do this by passing named argument to function
In [10]:
fibonacci_third(9,b=3)
Out[10]:
102
What we have to do if we want 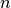 Fibonacci Numbers instead of
Fibonacci Numbers instead of 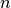 th Fibonacci Number?¶
th Fibonacci Number?¶
- One soulution is to return a list of
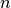 numbers. We will see
that once we learn about Lists in next chapter
numbers. We will see
that once we learn about Lists in next chapter - What we can do now is return an iterable object, that iterates
through
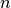 Fibonacci nuumbers. Instead of
Fibonacci nuumbers. Instead of returning a number, we can simplyyieldit to construct a genertor. The resulting Generator object can be used withforloop. (rememberrangeobject)
In [11]:
def fibonacci_generator(n,a=0,b=1):
first,second = a,b
while n != 0:
yield first
n, first, second = n - 1, second, first + second
In [12]:
for num in fibonacci_generator(10):
print(num,end=',')
0,1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34,
You can now also use in operator to check the membership of an
element in the Generator Object
In [13]:
8 in fibonacci_generator(10)
Out[13]:
True
In [14]:
10 in fibonacci_generator(10)
Out[14]:
False
Let’s modify above loop in order to print Fibonacci Numbers with numbering
In [16]:
for i,num in enumerate(fibonacci_generator(10,a = 2, b = 3)):
print('Fib({})={}'.format(i,num))
Fib(0)=2
Fib(1)=3
Fib(2)=5
Fib(3)=8
Fib(4)=13
Fib(5)=21
Fib(6)=34
Fib(7)=55
Fib(8)=89
Fib(9)=144
enumerate() function takes an iterable object as an argument and
returns an iterator which is the original iterator enumerated.